Applicable Products
Overview
This FAQ compares RAID synchronization times when creating a storage pool in QTS (using mdadm) and QuTS hero (using ZFS). It outlines architectural differences affecting synchronization speed and provides guidance for optimal setup.
- QTS (mdadm-based RAID): When you create a new RAID 1 volume, QTS uses the Linux mdadm utility, which performs a full initial synchronization (resync) of all data blocks, ensuring both drives are identical—even if no data has been written yet.
- QuTS hero (ZFS-based): QuTS hero uses ZFS, which only synchronizes data blocks as they are written. No lengthy initial resync is required for empty or newly created pools.
QTS RAID synchronization
- When you create a new RAID 1 group in QTS, the system uses the Linux mdadm utility to perform a full initial synchronization (resync) of all data blocks, even if no user data exists yet. This ensures both drives are fully identical.
- The RAID group is usable immediately, but performance may be reduced until resync finishes.
- To minimize delays, avoid heavy write operations during synchronization.
- Monitor the synchronization process via Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshots > Storage Pool Management.
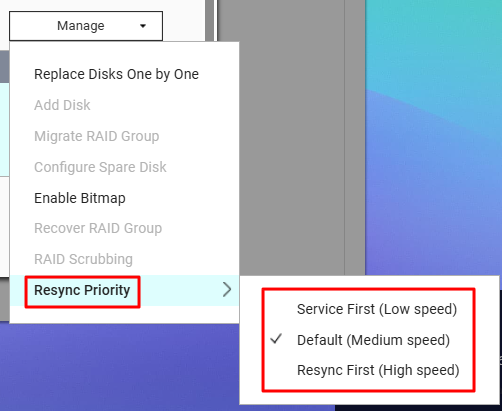
- You can adjust Resync Priority (Service First, Default, Resync First) to control sync speed versus system responsiveness.
QuTS hero RAID synchronization
- QuTS hero uses ZFS, which initializes mirrored pools quickly—no full-disk initial resync is required. Only data that you actually write is checked and mirrored.
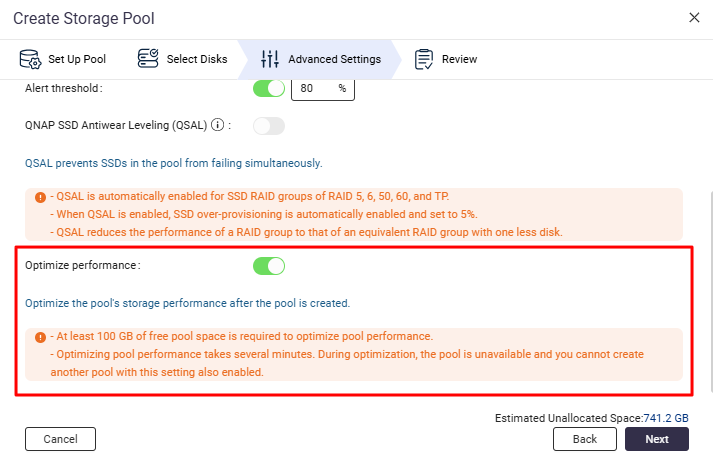
- If Optimize Performance is enabled during pool creation (default setting), the pool may be unavailable until optimization completes. This usually takes only a few minutes.
- ZFS automatically performs scrubs (background data integrity checks) and resilvering(rebuilding redundancy after a disk replacement), processing only data that actually exists, not the whole disk.
- Scrub: Verifies data integrity during normal operation.
- Resilver: Synchronizes new or replacement disks, but only used data is processed.
Recommendation
- Use identical disks (size and type) within a RAID group for best performance and compatibility.
- Minimize heavy workloads during RAID synchronization or initialization to reduce total sync time and avoid potential slowdowns.
- Regularly monitor the health and status of your storage pool using the management interface.
Further Reading
适用产品
概述
本常见问题解答比较了在 QTS 中创建存储池(使用 mdadm)和 QuTS hero(使用 ZFS)时的 RAID 同步时间。它概述了影响同步速度的架构差异,并提供了优化设置的指导。
- QTS(基于 mdadm 的 RAID):当您创建一个新的 RAID 1 卷时,QTS 使用 Linux mdadm 工具执行所有数据块的完整初始同步(重新同步),确保两个驱动器相同,即使尚未写入任何数据。
- QuTS hero(基于 ZFS):QuTS hero 使用 ZFS,仅在写入数据块时进行同步。对于空或新创建的池,不需要长时间的初始重新同步。
QTS RAID 同步
- 当您在 QTS 中创建一个新的 RAID 1 组时,系统使用 Linuxmdadm工具执行所有数据块的完整初始同步(重新同步),即使尚无用户数据存在。这确保了两个驱动器相同。
- RAID 组可以立即使用,但在重新同步完成之前性能可能会降低。
- 为减少延迟,请避免在同步期间进行大量写入操作。
- 通过以下方式监控同步过程存储与快照总管 > 存储 / 快照 > 存储池管理。
- 您可以调整重新同步优先级(服务优先、默认、重新同步优先)以控制同步速度与系统响应之间的平衡。

QuTS hero RAID 同步
- QuTS hero 使用 ZFS,能够快速初始化镜像池,不需要全盘初始重新同步。仅检查和镜像您实际写入的数据。
- 如果在池创建期间启用了优化性能(默认设置),则在优化完成之前池可能不可用。这通常只需几分钟。

- ZFS 自动执行清理(后台数据完整性检查)和重建(在更换磁盘后重建冗余),仅处理实际存在的数据,而不是整个磁盘。
- 清理:在正常操作期间验证数据完整性。
- 重建:同步新磁盘或替换磁盘,但仅处理已使用的数据。
建议
- 在 RAID 组中使用相同的磁盘(大小和类型)以获得良好的性能和兼容性。
- 在 RAID 同步或初始化期间尽量减少繁重的工作负载,以减少总同步时间并避免潜在的减速。
- 定期使用管理界面监控您的存储池的健康和状态。
进一步阅读





